Introduction

Pressure sensitive adhesives (PSAs) are a fascinating category of adhesives that bond surfaces upon the application of light pressure, without the need for heat or solvents. These versatile materials are used in an array of applications, from everyday tape to complex industrial solutions. Understanding their unique properties and types can help you make informed choices for your adhesive needs.
What Are Pressure Sensitive Adhesives
Pressure sensitive adhesives are designed to create a strong bond when applied with mere hand pressure, making them incredibly user-friendly. Unlike traditional adhesives, which often require curing or drying time, PSAs offer immediate adhesion, allowing for quick and efficient application. This characteristic makes them ideal for varied industries, including packaging, automotive, and electronics.
The Role of Pressure in Adhesion
The magic behind pressure sensitive adhesives lies in the role that pressure plays in creating a bond between surfaces. When pressure is applied to a PSA, it causes the adhesive to flow into the microscopic surface irregularities of the materials being bonded. This intimate contact enhances adhesion and ensures that the bond remains strong even under stress.
Types of Pressure Sensitive Adhesives
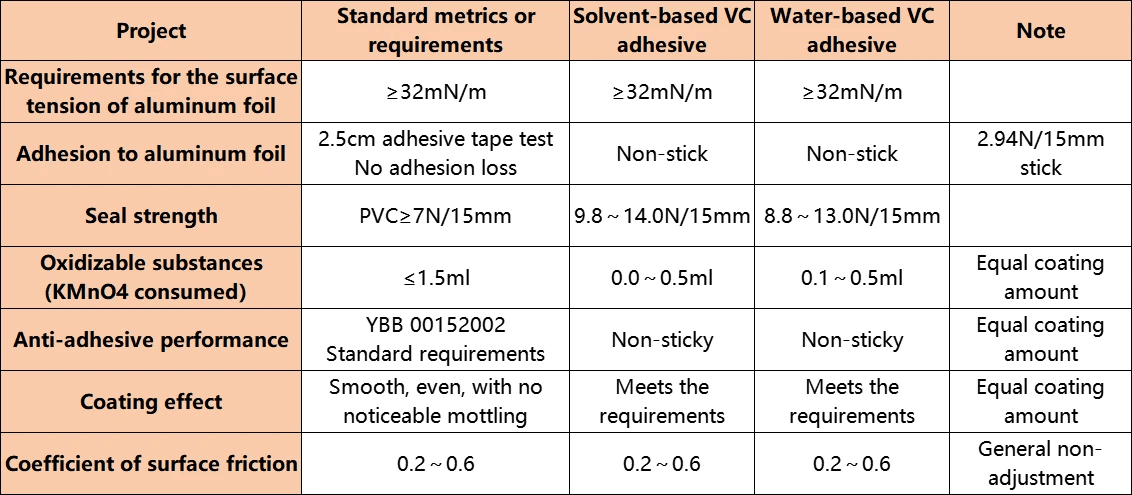
There are several types of pressure sensitive adhesives available on the market today, each with its own set of advantages and applications. Solvent-based adhesives offer robust bonding capabilities but come with environmental concerns; water-based options provide a more eco-friendly alternative without sacrificing performance. Additionally, hot-melt and UV-curable adhesives present innovative solutions tailored for rapid assembly processes and specific industry needs alike.
The Chemistry Behind Pressure Sensitive Adhesives
Understanding the chemistry behind pressure sensitive adhesives (PSAs) is crucial for anyone looking to grasp how these versatile materials function. At their core, PSAs are designed to bond quickly and securely when pressure is applied, making them ideal for a wide range of applications. The unique formulation of these adhesives involves various components that contribute to their effectiveness and usability.
Key Components of Adhesives
Pressure sensitive adhesives are primarily composed of polymers, tackifiers, and additives. Polymers form the backbone of the adhesive, providing flexibility and strength; common choices include acrylics and rubber-based materials. Tackifiers enhance the stickiness of the adhesive, ensuring it bonds effectively upon contact with surfaces; additives can also improve performance characteristics like UV resistance or thermal stability.
Solvent-based adhesives utilize solvents to dissolve the polymer matrix, allowing for easy application but requiring careful handling due to volatile organic compounds (VOCs). In contrast, water-based adhesives leverage water as a solvent, making them more environmentally friendly while still offering robust adhesion properties. Hot-melt adhesives take a completely different approach by using heat to melt solid polymers into a liquid state for application before cooling down to form a strong bond.
The Polymerization Process
The polymerization process is where the magic begins in creating pressure sensitive adhesives. This chemical reaction involves linking monomers together to form long chains or networks that give rise to the desired adhesive properties. Depending on whether you’re dealing with solvent-based, water-based, hot-melt, or UV-curable formulations, different polymerization techniques may be employed.
For instance, solvent-based PSAs often use free-radical polymerization or emulsion polymerization methods that allow for quick drying times once applied. Water-based systems typically rely on emulsion polymerization as well but require additional steps for curing after application. On the other hand, UV-curable adhesives utilize light energy in a photopolymerization process that rapidly solidifies the adhesive upon exposure to ultraviolet light—ideal for fast-paced production environments.
Properties that Matter
When selecting pressure sensitive adhesives for specific applications, certain properties become paramount: tackiness, shear strength, peel strength, and temperature resistance all play significant roles in determining performance. Tackiness refers to how quickly an adhesive will bond when pressure is applied; high tack is essential for applications like tapes or labels where immediate adhesion is necessary.
Shear strength indicates how well an adhesive can withstand forces parallel to its surface without failing—this property is critical in applications involving heavy loads or dynamic movements such as automotive parts assembly or packaging solutions using hot-melt adhesives. Lastly, temperature resistance ensures that your chosen PSA will maintain its integrity under varying environmental conditions; this property becomes particularly important in industries utilizing UV-curable technologies where exposure to heat could compromise performance.
Exploring Solvent-Based Adhesives

Solvent-based adhesives have long been a staple in the world of pressure sensitive adhesives, offering unique benefits that make them a popular choice for various applications. These adhesives utilize organic solvents to dissolve the adhesive materials, creating a viscous solution that can easily be applied to surfaces. The result is a strong bond that can withstand significant stress, making solvent-based options particularly appealing for demanding environments.
Advantages of Solvent-Based Adhesives
One of the primary advantages of solvent-based adhesives is their excellent bonding strength, which often surpasses that of water-based and hot-melt alternatives. This strength makes them ideal for applications requiring high-performance adhesion, such as automotive or industrial assembly tasks. Additionally, solvent-based formulations typically offer faster drying times compared to their water-based counterparts, allowing for quicker production cycles without compromising bond integrity.
Another perk is their versatility; solvent-based adhesives can adhere to a wide variety of substrates including metals, plastics, and wood. This adaptability opens up numerous possibilities across different industries where pressure sensitive adhesives are essential. Furthermore, many solvent formulations are resistant to moisture and temperature variations, enhancing durability in challenging conditions.
Common Applications and Uses
Solvent-based adhesives are commonly found in industries such as automotive manufacturing, construction, and packaging due to their robust performance characteristics. In automotive assembly lines, these adhesives are often used for bonding trim pieces or securing components that must endure vibrations and thermal fluctuations. Similarly, in packaging applications—especially those involving flexible materials—solvent-based options provide reliable seals that maintain product integrity during transport.
The versatility of these adhesives extends even further into electronics where they secure components on circuit boards or create durable bonds between dissimilar materials like glass and plastic. In woodworking shops, craftsmen rely on solvent-based pressure sensitive adhesives for projects requiring both speed and strength without the wait time associated with curing processes seen in UV-curable solutions.
Challenges and Safety Concerns
Despite their many advantages, solvent-based adhesives come with challenges that users must navigate carefully. One major concern is the volatile organic compounds (VOCs) released during application; these substances can pose health risks if inhaled over extended periods or if proper ventilation isn't maintained. Consequently, manufacturers have been under pressure to develop low-VOC formulations while still delivering effective bonding solutions.
Additionally, the flammability of solvents presents another challenge when working with these types of pressure sensitive adhesives; safety protocols need to be strictly followed during storage and application to prevent accidents in workplaces using these products extensively. Moreover, environmental regulations continue to tighten around VOC emissions which could impact future usage patterns as industries shift towards greener alternatives like water-based or UV-curable technologies.
The Rise of Water-Based Adhesives
Water-based adhesives have become a popular choice in various industries, primarily due to their eco-friendly nature and user-friendly properties. Unlike solvent-based adhesives, which often contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs), water-based options utilize water as the primary solvent, making them less harmful to both users and the environment. This shift towards water-based solutions is not just a trend; it's a response to increasing regulatory pressures and consumer demand for sustainable products.
Chemix's Water-Based Resin Solution
Chemix has developed an innovative line of water-based resin solutions that cater to the growing need for effective pressure sensitive adhesives without the drawbacks of solvents. These resins are designed to provide strong adhesion while remaining easy to apply and clean up, making them ideal for various applications. By focusing on water-based formulations, Chemix is leading the charge in creating pressure sensitive adhesives that meet both performance standards and environmental concerns.
Benefits for the Environment
One of the most significant advantages of water-based adhesives is their reduced environmental impact compared to solvent-based alternatives. With lower emissions of VOCs, these adhesives contribute less to air pollution and are safer for indoor use, making them a preferred choice in residential settings. Additionally, many manufacturers are now prioritizing sustainability by using renewable resources in their formulations, further enhancing the appeal of water-based pressure sensitive adhesives.
Versatility Across Industries
Water-based adhesives are incredibly versatile and find applications across various sectors such as packaging, textiles, automotive, and construction. Their ability to bond different materials while maintaining flexibility makes them suitable for everything from labels on packaging to upholstery in cars. As more industries recognize the benefits of switching from traditional solvent or hot-melt options to these advanced water-based solutions, we can expect continued growth in their adoption.
Hot-Melt Adhesives: Quick and Reliable

Hot-melt adhesives are a popular choice in various industries due to their quick application and reliable bonding capabilities. These adhesives are thermoplastic materials that become fluid when heated, allowing them to bond surfaces upon cooling. This unique property not only makes hot-melt adhesives easy to use but also allows for rapid production processes, making them particularly valuable in high-demand environments.
How Hot-Melt Adhesives Work
The magic of hot-melt adhesives lies in their composition and application method. When heated, these pressure sensitive adhesives transition into a viscous liquid that can be easily applied to surfaces; once cooled, they solidify to form a strong bond. The lack of solvents in hot-melt formulations means they cure quickly without the need for evaporation time, which is often required with solvent-based or water-based alternatives.
This fast curing process is particularly advantageous for manufacturers who need efficiency without compromising the quality of their products. Additionally, hot-melt adhesives exhibit excellent adhesion properties on various substrates, including plastics and paperboard—making them versatile for different applications. As industries continue to evolve towards faster production cycles, the demand for reliable hot-melt solutions is likely to increase.
Applications in Packaging and Assembly
Hot-melt adhesives find extensive use in packaging and assembly processes across multiple sectors. In packaging, they are often employed for sealing boxes or attaching labels due to their strong initial tack and durability under varying conditions. This makes them ideal for both consumer goods packaging as well as industrial applications where reliability is crucial.
Moreover, these adhesives are frequently utilized in assembly lines for products ranging from furniture to electronics. Their ability to bond quickly minimizes assembly times while maintaining structural integrity—a win-win situation for manufacturers looking to streamline production without sacrificing quality. The versatility of hot-melt adhesives ensures that they remain an essential component in modern manufacturing practices.
Pros and Cons of Hot-Melt Solutions
While hot-melt adhesives offer numerous advantages, they also come with certain drawbacks that users should consider before selecting this type of adhesive over solvent-based or water-based options. On the plus side, these pressure sensitive adhesives provide quick bonding times and excellent flexibility once cured—ideal traits for dynamic applications such as packaging or product assembly where speed matters most.
However, one notable downside is their sensitivity to temperature changes; exposure to extreme heat can weaken bonds formed by hot melts if not properly managed during storage or transportation processes. Furthermore, while they perform well on many substrates, some materials may require specific formulations or surface treatments for optimal adhesion performance—potentially complicating selection processes.
In conclusion, hot-melt adhesives present a compelling option within the realm of pressure sensitive adhesives due to their speed and adaptability across various applications—from packaging solutions that keep products secure during transit to assembly lines demanding efficiency at every turn.
UV-Curable Adhesives: A Revolutionary Approach

UV-curable adhesives represent a significant leap in adhesive technology, setting themselves apart from traditional options like solvent-based, water-based, and hot-melt adhesives. The defining feature of UV-curable adhesives is their ability to cure rapidly when exposed to ultraviolet light, allowing for instant bonding without the need for heat or long drying times. This innovative approach not only enhances efficiency but also opens up new possibilities in various applications.
What Makes UV-Curable Different
Unlike solvent-based and water-based adhesives that rely on evaporation or absorption for curing, UV-curable adhesives undergo a photochemical reaction triggered by UV light. This unique mechanism allows them to form strong bonds almost instantly, which is particularly beneficial in high-speed production environments. Additionally, the absence of solvents means that these adhesives can be formulated to be low in volatile organic compounds (VOCs), making them a more environmentally friendly option compared to traditional pressure sensitive adhesives.
Benefits in Fast-Curing Applications
One of the standout advantages of UV-curable adhesives is their speed; they can go from liquid to solid within seconds when exposed to UV light. This rapid curing process significantly reduces production times and increases throughput, making them ideal for industries where time is money—think packaging and electronics assembly. Moreover, their ability to cure on-demand helps minimize waste and ensures that only the required amount of adhesive is used during manufacturing.
Industries Embracing UV Technology
The versatility of UV-curable adhesives has made them popular across various industries including automotive, electronics, and medical devices. Companies are increasingly recognizing the benefits of using these fast-curing solutions over conventional methods like solvent and hot-melt adhesives due to their efficiency and performance characteristics. As more businesses seek sustainable practices without compromising quality, the adoption of UV technology continues to rise as an essential component in modern adhesive formulations.
Conclusion
In wrapping up our exploration of pressure sensitive adhesives, it’s clear that these versatile materials play a crucial role across various industries. From solvent-based options to innovative UV-curable solutions, each type has unique properties and applications that cater to different needs. Understanding the nuances of pressure sensitive adhesives helps in making informed decisions for projects requiring reliable adhesion.
Key Takeaways on Pressure Sensitive Adhesives
Pressure sensitive adhesives are remarkable in their ability to bond without the need for heat or solvents, relying instead on pressure alone. The spectrum of options—including solvent-based, water-based, hot-melt, and UV-curable adhesives—offers something for every application, whether it’s packaging or assembly. Each type brings its own set of advantages and challenges, making it essential to match the adhesive with the specific requirements of your project.
Choosing the Right Type for Your Needs
When selecting a pressure sensitive adhesive, consider factors such as environmental impact, curing time, and application method. For instance, solvent-based adhesives might be ideal for heavy-duty applications but come with safety concerns; meanwhile, water-based alternatives are more eco-friendly and versatile across industries. Hot-melt adhesives offer quick bonding solutions but may not suit all conditions; UV-curable options shine in fast-paced environments where speed is paramount.
Future Trends in Adhesive Technologies
The landscape of adhesive technologies is evolving rapidly with a growing emphasis on sustainability and efficiency. Water-based and UV-curable pressure sensitive adhesives are gaining traction as industries seek greener alternatives that do not compromise performance. As innovation continues to drive advancements in this field, we can expect even more sophisticated formulations that enhance durability while minimizing environmental impact.
